Comparison of methods
In my earlier post, I had mentioned two approaches to count people. So, I have gone through the proposed methods namely:
As I have already mentioned, CSRNet and SS-DCNet are suited to cases when we have footage that is from within the room by keeping a running count of the number of people in the room frame-by-frame. Both these networks work well for densely crowded places. Given below is my analysis of the two.
CSRNet
The Congested Scene Recognition called CSRNet provides a data-driven and deep learning method that can understand highly congested scenes and perform accurate count estimation as well as present high-quality density maps. The CSRNet is composed of two major components: a convolutional neural network (CNN) as the front-end for 2D feature extraction and a dilated CNN for the back-end, which uses dilated kernels to deliver larger reception fields. CSRNet is an easy-trained model because of its pure convolutional structure.
SS-DCNet
The main motivation behind this CNN based counting technique is that a dense region can always be divided until sub-region counts are within the previously observed closed set. It introduces the idea of spatial divide-and-conquer (S-DC) that transforms open-set counting into a closed-set problem. This idea is implemented by a novel Supervised Spatial divide-and-Conquer Network (SS-DCNet). SS-DCNet can only learn from a closed set but generalizes well to open-set scenarios via S-DC. To avoid repeatedly computing sub-region convolutional features, S-DC is executed on the feature map instead of on the input image.
The SS-DCNet is implemented as two types, i.e.:
- Regression-based Counter: R-Counter directly regresses count values within the closed set. If predicted count values are greater than Cmax, the predictions will simply be truncated to Cmax.
- Classification based counter: Instead of regressing open-set count values, C-Counter discretizes local counts, and classifies count intervals. Specifically, an interval partition of [0, +∞) is defined as {0}, (0, C1], (C2, C3], … ,(Cm-1, Cmax] and (Cmax, +∞). These M + 1 sub-intervals are labeled to the 0-th to the M-th classes, respectively. For example, if a count value falls into (C2, C3], it is labeled as the 2-nd class. The median of each sub-interval can be adopted when recovering the count from the interval.
Given below is a comparison of these methods
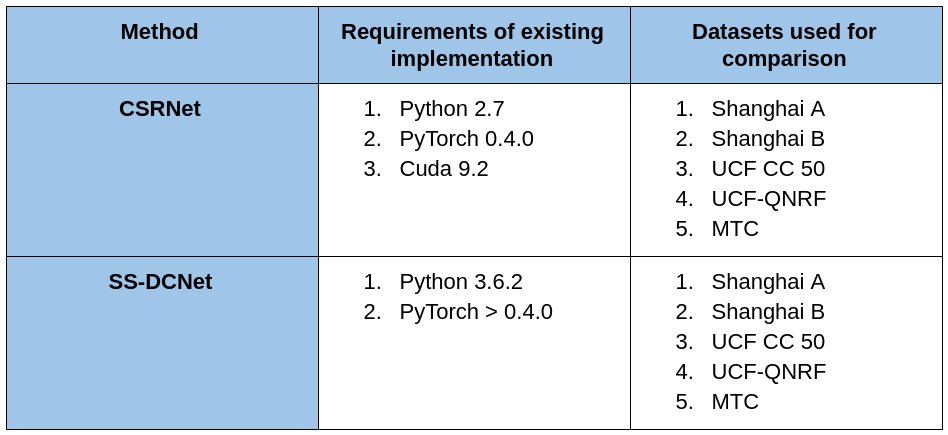
Requirements of existing implementations of the methods
Given below is a comparison of their performances in terms of MAE (Mean Absolute Error) and MSE (Mean Square Error)
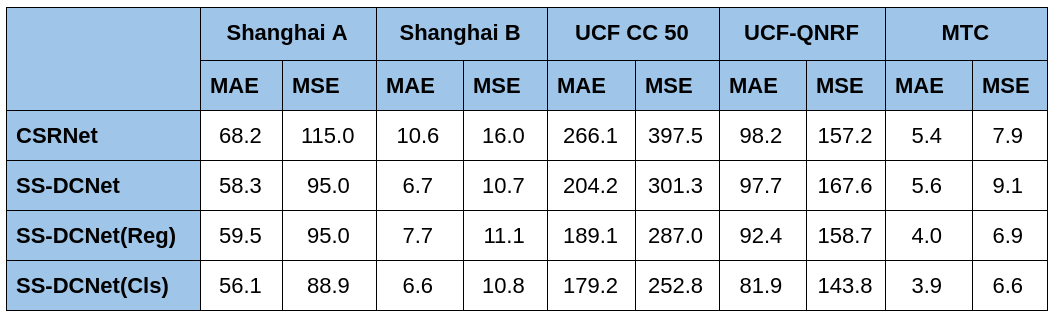
Comparison of performances
On looking at the MAE of both these methods it is clear that SS-DCNet performs better. Therefore, it is my preferred choice. This, however, may not be a very viable option if there are too many rooms in the building and each room needs to be fitted with a camera. Sometimes owing to the size of the rooms, it might be the case that a single camera is not enough to cover the entire room, So getting the count of people in the room from multiple views requires preprocessing before being passed through the network of choice.
I intend to use the following pre-processing step:
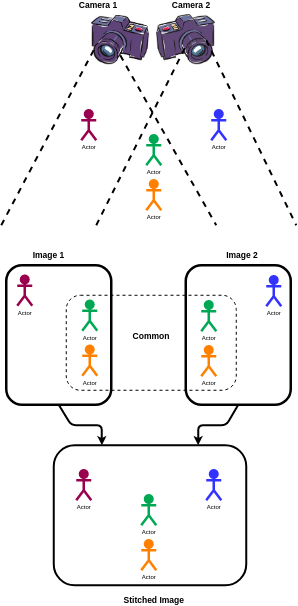
Pre-processing step for multiple views
Since this may not be a viable option for a building with a lot of rooms, I also propose another approach to track people entering and leaving the building using the cameras at entrances.
Therefore, I intend to go with a Deep-SORT based approach to track people and compare it with the existing baseline. I will also look at some more approaches on the same lines as Deep-SORT just to be sure that I have what works the best.